Energetically efficient ventilation ducts
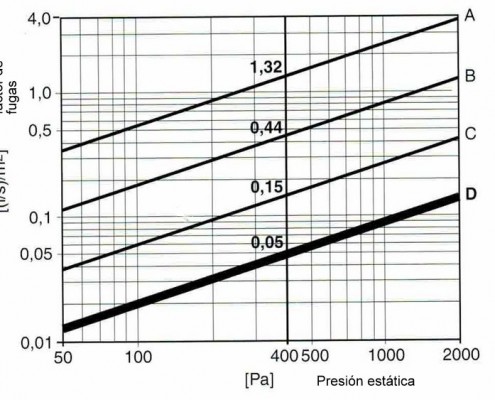
On occasion we talked type vents attending to degree of watertightness thereof. The standard defines four levels A,B,C y D. But, What is the importance of a ventilation system has one kind or another sealing?
In recent years there has been a steady increase in energy demands, both residential and industrial. And an important part of the energy consumption is produced by buildings.
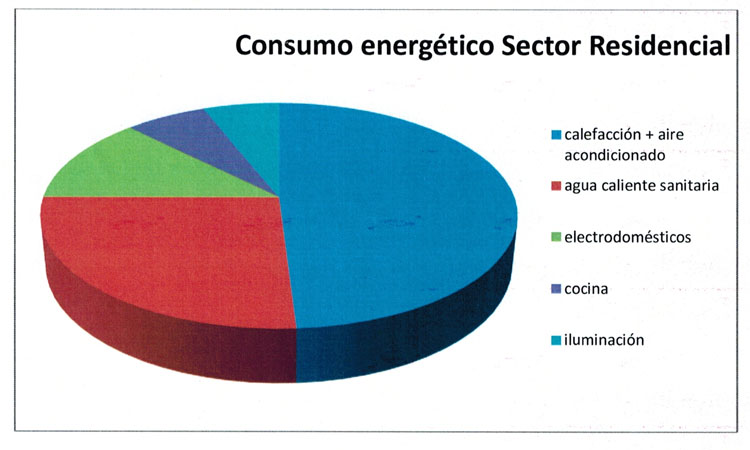
The percentage of air conditioning energy consumption of a residential building is around 48%, representing increased energy expenditure and control of strategic importance.
Increased energy consumption represents a major operating cost and a higher level of CO2 emissions.
Last Kyoto Agreement, and requires all countries adhering to rationalize energy consumption in order to achieve lower emissions of carbon dioxide and improve environmental sustainability. For this purpose, the European Union issued a directive requiring member countries to work forcefully to promote buildings with more energy efficient systems.
Regarding ventilation and air conditioning ducts There are two ways to improve the energy performance of the same. Better insulation can be up to 75% energy costs and 25% for improving the sealing of the ducts.
The article in your IT RITE 1.2.4.2.3 of 29/8/2007 determines ductwork must have a corresponding sealing to class B or higher, depending on application.
Generally, ventilation systems consist of a Ductwork of different types (rectangular, circular, Flexible etc ...) that give the system an average level of tightness of type B.
The effort would represent conduits adapted to a higher standard sealing, for example of type C or D, could represent an energy savings of up to 67 and 95% respectively according to the circumstances of each installation.
Improving ducts allow a sensible energy saving, lowering the operating costs of the facilities. But also, moving equipment would be smaller air, lower air treatment and even the dimension of the ducts themselves.
A change of this nature, move from B to C sealing would save at European level the order of 10TW h, or what is the same, could be close 3 NPPs midlevel.